Tired of flickering LED strips and unpredictable dimming? The problem might not be your LEDs—but your driver.
A constant voltage TRIAC dimmable LED driver provides a fixed 12V or 24V DC output and enables smooth dimming using standard wall dimmers with leading edge (phase-cut) control.

Confused by different driver types or frustrated by inconsistent dimming? In this post, I’ll break down how constant voltage TRIAC dimmable drivers work, when to use them, and how to avoid common mistakes.
What Is a Constant Voltage LED Driver?
Many lighting problems begin with the wrong power source. A constant voltage driver might be exactly what your LEDs need.
A constant voltage LED driver outputs a steady DC voltage, typically 12V or 24V, regardless of the current drawn by the LEDs.
Why Use Constant Voltage?
Unlike constant current drivers that regulate amperage, constant voltage drivers deliver a fixed output voltage. These are ideal for LED products that have built-in resistors or current regulation—like LED strips and modules.
Key Characteristics
| ลักษณะเฉพาะ | คำอธิบาย |
|---|---|
| แรงดันขาออก | Fixed at 12V or 24V DC |
| Load Regulation | Maintains voltage regardless of LED load |
| Applications | LED strips, signage, cabinet lighting |
| Wiring | Parallel connection to multiple LEDs |
If you’re using products where the current is internally regulated, a constant voltage driver ensures the system is simple and scalable.
Understanding TRIAC Dimming: Leading Edge Phase-Cut Control
Dimmers aren’t all the same—and neither are the drivers that work with them.
TRIAC dimming uses leading edge phase-cut control to reduce the power delivered to LEDs, making it possible to adjust brightness using standard wall dimmers.
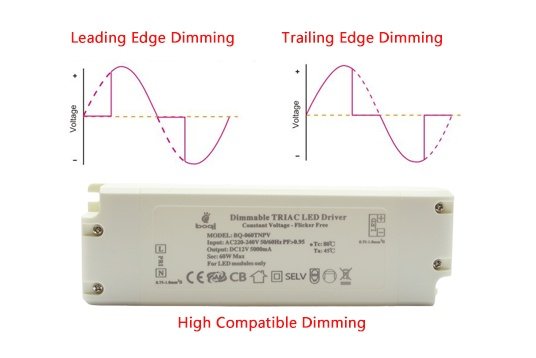
How TRIAC Dimming Works
TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) is a semiconductor device used in traditional AC dimmers. It chops the AC waveform at the beginning of each cycle (leading edge), reducing the average voltage reaching the driver.
What This Means for LED Drivers
TRIAC dimmable drivers must detect and respond to this chopped AC waveform. Inside, the driver converts the modified AC signal to a clean DC voltage, while adjusting output power to match the dimming signal.
| พารามิเตอร์ | TRIAC Dimmer |
|---|---|
| Type | Leading edge phase-cut |
| Compatibility | Traditional wall dimmers |
| Dimmer Load | Minimum and maximum load required |
| Signal Type | Chopped AC sine wave |
When everything is matched correctly, TRIAC dimming offers a cost-effective and widely compatible way to control LED brightness.
How a Constant Voltage TRIAC Dimmable Driver Works
Here’s where everything comes together—the driver is the bridge between the dimmer and your LEDs.
A constant voltage TRIAC dimmable driver converts chopped AC power into regulated 12V or 24V DC, and modulates the output based on the dimming signal.
What Happens Inside?
Inside the driver, there are key functional blocks:
- Input Stage: Handles the AC input from the TRIAC dimmer, including filtering and surge protection.
- Phase Detection: Interprets the leading-edge chopped waveform to calculate dimming level.
- Conversion Stage: Converts AC to DC while adjusting output power based on dimming input.
- Output Stage: Delivers regulated 12V or 24V DC to the LED load.
Why Matching Matters
If the LED load voltage doesn’t match the driver output (e.g., 12V LEDs with a 24V driver), performance issues like flicker, reduced lifespan, or even damage can occur.
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Phase-cut Detection | Tracks dimmer angle |
| Switching Converter | Adjusts DC output based on phase angle |
| Constant Voltage Regulator | Maintains fixed output voltage |
Getting this right is crucial for stable, dimmable LED performance.
Key Specifications: Voltage, Wattage, and Load Range
Even the best driver fails if you choose the wrong specs.
For reliable performance, match the driver’s output voltage to the LED load, stay within the wattage range, and meet the dimmer’s minimum load requirements.

What to Look For
| Spec | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| แรงดันขาออก | Must match LED load (12V or 24V) |
| Output Power | Must handle total LED wattage |
| Load Range | Impacts dimming smoothness and compatibility |
| แรงดันไฟฟ้าขาเข้า | Must match your region (e.g. 120V AC in Canada) |
| ช่วงลดแสง | Should go low enough without flicker |
If your LED load is too low, the dimmer may not even detect it. If it’s too high, you risk overheating the driver.
A good rule: operate the driver at 80% of its max rated power for safety and longevity.
Typical Applications: LED Strips, Modules, and Architectural Lighting
Where do TRIAC dimmable constant voltage drivers shine?
They are perfect for residential, commercial, and decorative lighting applications using 12V or 24V LED systems.

Where I Use Them
In my projects, I’ve used constant voltage TRIAC dimmable drivers in:
- LED strip installations under cabinets or stairs
- Retail lighting with wall dimmers
- Architectural cove lighting
- Signage and display lighting in shopping malls
- Residential accent lighting
These setups benefit from:
- Smooth wall-dimmer control
- Easy scalability
- Wide availability of LED products
| แอปพลิเคชัน | Why Use TRIAC Dimmable Driver |
|---|---|
| LED Strips | Flexible, low-voltage, often need dimming |
| Signage | Simple brightness control |
| Accent Lighting | Seamless integration with home dimmers |
If you want flicker-free ambiance, these drivers do the job well.
Benefits of Using Constant Voltage TRIAC Dimmable Drivers
Why choose this over other dimming methods?
They offer simple integration with existing wall dimmers, affordable setup, and reliable dimming without complex control systems.
Practical Advantages
- No need for extra controllers
- Compatible with most residential wiring
- Works with standard TRIAC dimmers
- Cost-effective for large installs
- Easy to source and replace
I’ve found that in retrofit projects, this type of driver lets you upgrade to LED without changing your existing dimming infrastructure.
Compatibility: Matching with Dimmers and LED Loads
Don’t mix and match blindly—compatibility is everything.
The TRIAC dimmable driver must match the dimmer’s technology and the LED load’s voltage and current requirements for flicker-free performance.
Key Considerations
| Item | What to Check |
|---|---|
| Dimmer Type | Must be leading-edge phase-cut (TRIAC) |
| Minimum Load | Dimmer must detect the driver at low output |
| LED Load Voltage | Match exactly with driver’s output |
| Number of Drivers | Avoid overloading a single dimmer |
Some smart dimmers are not compatible with TRIAC drivers. In those cases, check with the manufacturer or switch to an ELV or 0-10V system.
Common Issues: Flickering, Inrush Current, and How to Avoid Them
Even a good setup can go wrong. Let’s fix that.
Flicker, inrush current, or dropout usually result from poor dimmer-driver compatibility, incorrect wiring, or mismatched load values.
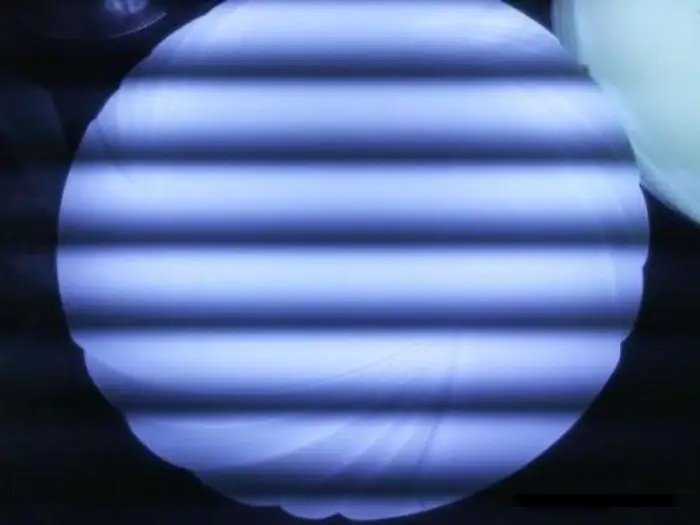

Troubleshooting Tips
- Flickering at low dim levels? Check dimmer compatibility and minimum load.
- Lights don’t turn on? The dimmer might not detect the driver—try increasing the load.
- Buzzing noise? Could be inrush current—use drivers with soft-start circuits.
| Problem | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Flickering | Incompatible dimmer or low load | Use tested dimmer; increase load |
| No Dimming | Smart dimmer or mismatched driver | Check dimmer type and driver specs |
| Light Dropout | Inrush or unstable line input | Use driver with inrush protection |
These issues are avoidable if you choose reliable drivers and pair them carefully.
Installation Guidelines: Wiring and Setup Tips
Even the best driver fails with poor wiring.
Always connect the driver to the correct AC input, ensure polarity on the DC side, and follow safety guidelines during installation.

Tips for Installers
- Always match input voltage (e.g. 220V in EU)
- Connect TRIAC dimmer before the driver on the AC side
- Use proper gauge wire for load
- Mount in a ventilated area to avoid overheating
- Observe polarity: + to + and – to –
I’ve seen many projects go wrong simply because of reversed polarity or miswired dimmers. Double-check before powering up.
Constant Voltage vs. Constant Current: What’s the Difference?
This is a key decision in LED system design.
Constant voltage drivers deliver fixed voltage, while constant current drivers regulate output current—each is for a different kind of LED load.

Choose Based on LED Type
| Driver Type | เอาท์พุต | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| Constant Voltage | Fixed Voltage | LED strips with resistors |
| Constant Current | Fixed Current | High-power LEDs, COBs, spotlights |
Using the wrong type can cause damage or malfunction. Know your load.
Why boqi: Reliable TRIAC Drivers with CE, RoHS, and Custom Options
I started boqi to help others avoid the pain of unreliable drivers.
At boqi, we offer certified TRIAC dimmable drivers with CE, RoHS compliance, wide voltage options, and flexible OEM/ODM solutions.
Whether you’re managing a large project or need custom specs, we support you with:
- 12V and 24V TRIAC dimmable drivers
- Wide wattage options from 15W to 300W
- CE, SAA, CB and RoHS compliant models
- Customization for dimming curves, enclosures, and cables
I’ve seen firsthand how quality drivers reduce support calls, returns, and headaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a TRIAC dimmable driver with a smart dimmer?
Only if the smart dimmer uses leading-edge phase-cut. Some use PWM or trailing-edge—check specs.
What happens if I overload the driver?
It may overheat or shut down. Always keep the load below 80–90% of max rated power.
Can I connect multiple LED strips to one driver?
Yes, as long as the total wattage stays within range and all strips are 12V or 24V to match the driver.
Why do my lights flicker at low dimming levels?
This often means the load is too small or the dimmer is not compatible. Try a load resistor or use a tested dimmer.
Conclusion
A constant voltage TRIAC dimmable LED driver is a reliable and affordable way to control LED brightness—if you match it correctly with the dimmer and LED load.









