Naviguer dans les méandres de la Pilote de LED La sélection est un sujet d'une importance considérable dans le domaine de l'électronique et de l'éclairage. À première vue, le processus peut sembler simple. Cependant, le choix d'un pilote approprié qui s'aligne parfaitement avec un produit d'éclairage optimisé exige une attention méticuleuse.
En réalité, la procédure comprend plusieurs étapes. Il est impératif d'examiner méticuleusement chaque étape décrite, en particulier si l'objectif est d'identifier un pilote qui réponde aux exigences de forme d'onde de tension et de contrôle de phase d'un système de lampe LED sophistiqué.
1. Détermination de la demande
Tout d'abord, il est impératif de déterminer si vous êtes à la recherche d'un pilote d'extérieur ou d'intérieur. Bien que le terme "driver extérieur" puisse suggérer une exclusivité pour les environnements extérieurs, il se rapporte généralement à un indice d'étanchéité IP66 ou supérieur, associé à un indice de protection contre les surtensions en mode différentiel de 2 kV et en mode commun de 4 kV. Les circuits d'attaque extérieurs trouvent principalement leur place dans les éclairages de baie et les éclairages antidéflagrants. Inversement, les drivers intérieurs, lorsqu'ils sont équipés d'une protection robuste contre les surtensions, peuvent être adaptés à un usage extérieur. Néanmoins, les termes "extérieur" et "intérieur" restent les descripteurs les plus courants pour les applications d'éclairage.

2. Mode courant constant ou tension constante
Dans le domaine de l'électronique et de l'éclairage, le choix entre le mode courant constant (CC) et le mode tension constante (CV) pour les pilotes de LED est crucial. Le mode CC garantit un courant constant, essentiel pour que les LED conservent une luminosité et une longévité uniformes. À l'inverse, le mode CV, idéal pour les configurations avec plusieurs LED ou bandes en parallèle, fournit une tension de sortie fixe. Dans ce cas, chaque LED ou bande tire le courant nécessaire de cette source de tension, mais il est essentiel que chacune dispose de son propre mécanisme de limitation de courant. Le choix entre CC et CV dépend des exigences du système d'éclairage : Le mode CC met l'accent sur la précision pour les LED individuelles, tandis que le mode CV met l'accent sur la flexibilité pour les installations plus importantes. Il est essentiel de comprendre ces modes pour obtenir des performances optimales du système d'éclairage à LED.


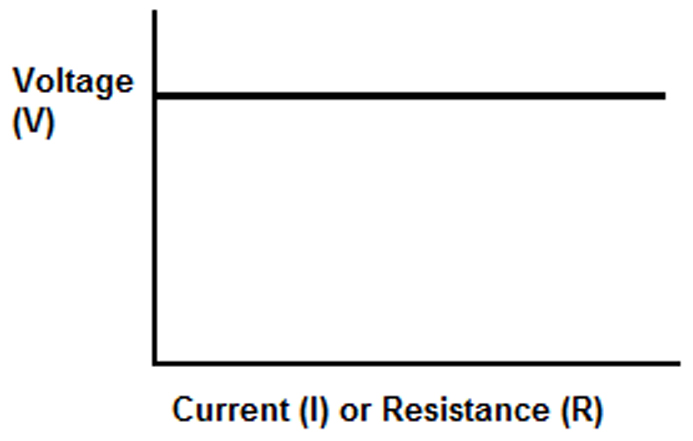
3. Sélection de la puissance nominale:
Pour les lampes à LED, la puissance nominale fait invariablement référence à la puissance d'entrée. Cependant, lorsqu'il s'agit de pilotes de LED, on se réfère à la puissance de sortie, qui est le produit du courant de sortie et de la tension de sortie maximale. L'essentiel est de s'assurer que la puissance choisie est supérieure à la puissance de charge maximale de la LED.
4. Spécification de la tension de sortie
Le choix de la bonne spécification de tension de sortie pour un pilote de LED est crucial pour la performance optimale et la longévité des systèmes d'éclairage à LED. Le pilote de LED sert d'alimentation pour la LED, convertissant la puissance d'entrée en tension, courant et fréquence corrects requis par la LED. Lors du choix d'un pilote de LED, il faut s'assurer que sa tension de sortie correspond aux exigences de tension de la LED ou de la matrice de LED qu'il alimente. Des tensions inadaptées peuvent entraîner une baisse de la luminosité, des changements de couleur, un scintillement, voire une défaillance prématurée de la LED. En outre, il est essentiel de tenir compte de l'environnement d'exploitation, car les exigences en matière de tension peuvent varier en fonction des fluctuations de température. Certains pilotes de LED avancés sont dotés d'une tension de sortie réglable, ce qui permet de s'adapter à diverses applications. En conclusion, en choisissant soigneusement la tension de sortie d'un pilote de LED, on peut garantir une utilisation efficace de l'énergie, une qualité de lumière constante et une durée de vie prolongée du système de LED.
5. Spécification du courant de sortie
Cette étape est cruciale et dépend en grande partie du type de puce LED choisi et de son point de fonctionnement optimal. Souvent, le courant souhaité n'est pas disponible dans les listes de modèles de pilotes. Dans ce cas, deux possibilités s'offrent à vous : sélectionner le modèle disponible le plus proche ou contacter le fabricant du pilote pour obtenir un modèle spécifique. La première solution est immédiate, mais risque de compromettre les performances lumineuses, tandis que la seconde, bien qu'elle puisse prendre du temps, garantit un produit final optimal. Le choix dépend invariablement de la stratégie de marché du fabricant et des circonstances spécifiques.
Si vous n'êtes pas sûr de la spécification du pilote de LED dont vous avez besoin, essayez d'utiliser notre Calculateur de pilote de LED!

6. Décision relative au type de câble
Sur le marché nord-américain, les câbles UL, principalement dotés d'une gaine en PVC, sont la norme. En revanche, les autres régions du monde ont tendance à privilégier les câbles VDE avec des gaines en caoutchouc. Il convient de noter que les câbles UL sont acceptés dans le monde entier, mais qu'ils sont soumis à des restrictions en tant que conducteurs autonomes dans le cadre des normes CE. Les normes CEI introduisent les appareils de classe II, dépourvus de connexion à la terre. Lors de l'intégration de connecteurs, il est essentiel de connaître leurs certifications. Les connecteurs certifiés UL peuvent être coûteux, ce qui incite certains à opter pour des boîtes de jonction pour les connexions, en particulier en Amérique du Nord.
7. Sélection de la certification
Les certifications sont primordiales. Pour le marché de l'UE, la certification CE est une condition préalable, tandis que la certification UL est fondamentale ailleurs. L'ENEC est souvent considéré comme supérieur dans de nombreuses régions. La certification CB est importante car elle peut être facilement convertie en KC, PSE ou SAA pour une somme modique. En Amérique du Nord, la classe 2 peut simplifier la conception de l'éclairage, tout comme la SELV dans d'autres pays.
8. Choix de la méthode de gradation
Cette phase peut s'avérer complexe pour les éclairagistes, étant donné que leur expertise s'oriente souvent davantage vers la mécanique de l'éclairage que vers l'électronique et le contrôle. Il est essentiel de déterminer le besoin d'une fonction de gradation et sa réalisation, que ce soit par le biais de TRIAC / Coupe de phase, 0-10V, DALIou PWM. Le choix de protocole de contrôleChacun de ces protocoles a ses avantages et ses limites, selon qu'il s'agit d'un nouveau projet ou d'une modernisation. Un examen plus approfondi de ces protocoles fera l'objet d'un article ultérieur.

9. Vérification des échantillons
Une fois la conception électrique achevée, le voyage n'est pas terminé. L'étape suivante consiste à acquérir et à valider des échantillons de votre système d'éclairage. Il est conseillé de commander des échantillons par lots, initialement de 2 à 3 unités, afin d'évaluer la cohérence du produit. Une fois les tests de performance électrique réussis, un lot plus important peut être commandé pour un essai pilote. La taille recommandée pour un tirage unique est supérieure à 50 unités. En outre, il est essentiel pour les deux parties de comprendre les délais de livraison des produits, en particulier pour les commandes en gros, afin de garantir une production sans faille.
10. Évaluation de la qualité et des services
Avant de prendre votre décision, il est impératif d'examiner la garantie, d'évaluer la qualité du service à la clientèle et la capacité du vendeur à comprendre les besoins du client. Ces facteurs jouent un rôle essentiel pendant et après la transaction.
boqi LED Driver adhère méticuleusement aux étapes susmentionnées, s'efforçant de collaborer avec vous à chaque étape. Notre objectif est d'appréhender vos besoins de manière globale et de vous présenter la solution la plus appropriée. Nous espérons établir une relation durable. Pour d'autres produits haut de gamme, consultez nos offres.

Un tutoriel vidéo est également disponible pour ceux qui préfèrent une expérience d'apprentissage visuelle.







