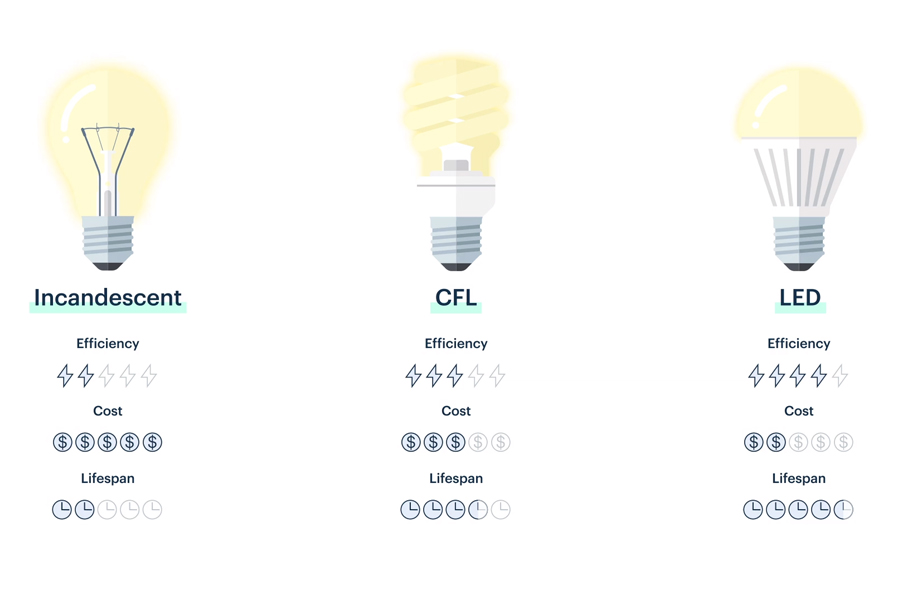
LED lights are everywhere these days. They save a lot of energy but aren’t as good as old bulbs in showing true colors or dimming.

Now, there’s a new tech called TRIACs used in dimmers. These are replacing other light types in homes where old bulbs are still common. In simple words, TRIACs are often part of these lights.
LEDs need to use less energy and last long to be the best. Even with cheap parts, they can manage powerful devices well. This shows TRIAC is great for lights and other key electrical items that need to be reliable.
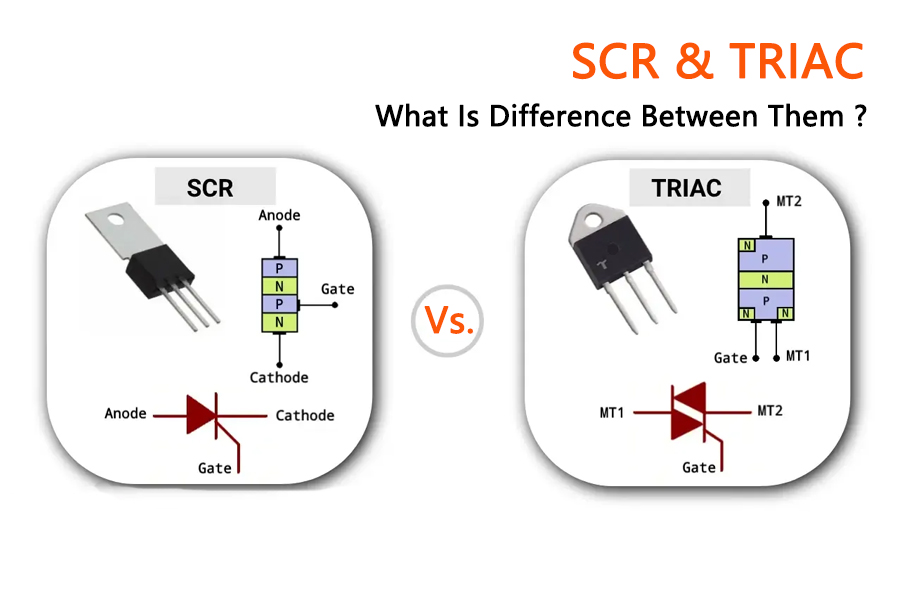
What’s a TRIAC?
TRIAC is an electronic part with three connectors that can move current two ways when turned on. Think of it like two SCRs connected in a unique way.
To turn it on, a TRIAC needs a gate signal like what’s in an SCR. Its main use was to better manage AC power.
There are many TRIAC types to choose from. They’re made to handle different power levels and stay safe. But, most TRIACs handle less than 50 A, which is less than SCRs. So, they aren’t good for very high power needs. TRIACs are really useful. They can work with both plus and minus power ends, making them super handy. This means they can be used in many designs. While SCRs can move current two ways, they aren’t as good with low power as TRIACs. So, TRIACs are a better pick for most people.
How TRIAC Dimming Works
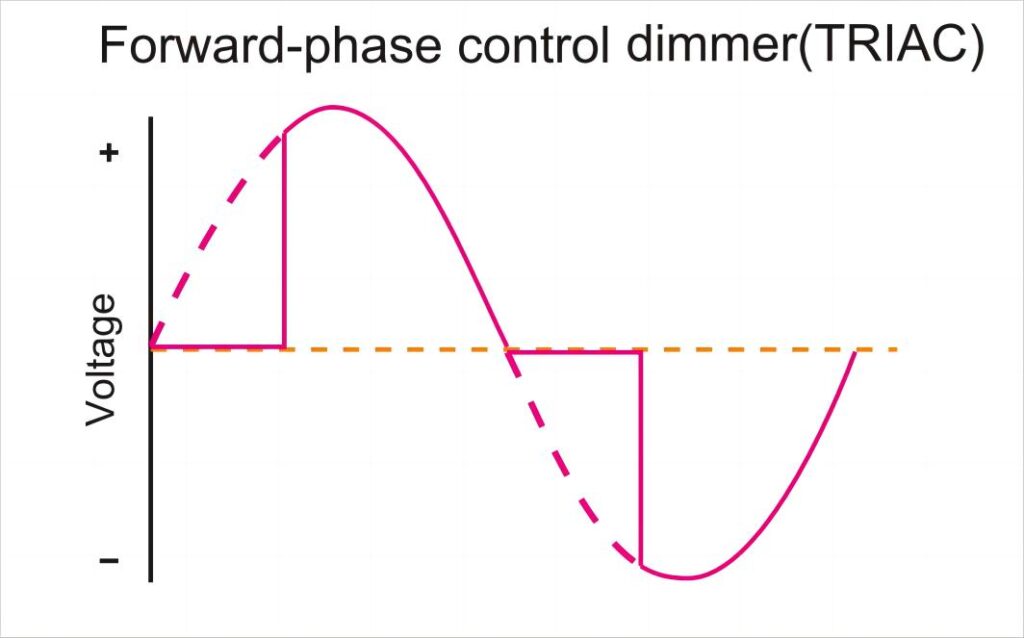
Starting at AC phase 0, dimming starts by lowering input voltage till the TRIAC dimmer works. This keeps up until output voltage matches what’s needed. This dimming changes the AC’s effective value. The first part adjusts the angle for each AC half-wave.
Simply put, TRIAC dimming tools act like fast switches, helping decide the current in an LED light. When turned on, it controls electron flow inside.
Usually, this means cutting off the voltage shape, stopping the electricity. This stop happens when the load is full.
A cool thing about the TRIAC tool in LED lights is how it can change light levels. Because the switch is a bit slow, power goes down, making the bulb less bright.
How fast the switch works shows how much energy is used. A quick switch uses more energy. But a slow switch uses less energy, making the LED a bit dim. The good part of TRIAC dimming is it doesn’t easily break or flicker.
Unlike other dimmers, TRIAC dimming is good for LED bulb life. This is done by using two-way voltage on the TRIAC’s gate, controlling electricity. When on, the TRIAC lets power through, but stops if current gets too low.
The circuit is good with high voltage, but control currents stay low. The TRIAC circuit, with phase control, adjusts the current in a circuit load.
If you’re using an LED with a TRIAC dimmer and want a TRIAC dimming LED driver, make sure the dimmer is a real TRIAC device.
Some TRIAC dimmers work best with resistive loads. But wrong pairing of an LED and a TRIAC dimmer might cause issues like noise or flicker. If not fixed, this could shorten LED light life.
Why Choose TRIAC?
TRIACs are known to handle large voltages and are used in many electric control systems. This shows that TRIACs are good for controlling lights, something we do every day.
TRIAC circuits are flexible and have many ways to control and switch AC power. For instance, they can power small motors and fans. The TRIAC system is simple but offers varied control, making it useful for many.
TRIAC Controller & Receiver’s Job in Lights
De TRIAC controller is a detailed way to adjust different light features. It works by quickly changing the electric current’s way, making a dim effect. This isn’t just for LEDs, but for other lights too.
In big power uses, like lighting or heating, TRIACs are the first choice. They turn on and off faster than normal switches, reducing unwanted sounds and electronic noise (EMI).
Using a TRIAC receiver lets you adjust the power sent to a device. This is done by always checking the voltage at the TRIAC ends and turning on the device when the voltage is right.
LEDs, also known as light-making parts, are popular because they save energy, last long, and give strong light.

Sure, here’s the content formatted as per your request:
How TRIAC Dimmers Fit in LED Systems
LEDs, also known as light-making parts, are now loved for their low energy use, long life, and strong light. Yet, adjusting their brightness can be hard. This is when TRIAC dimmers help.
By changing the current, TRIAC dimmers adjust light. They switch quickly between on and off states, keeping the current steady. This makes them perfect for dimming LEDs.
But, using TRIAC dimmers with LEDs can be tricky. Before setting up an LED, check if it fits with the dimmer. Next, see if the dimmer can manage the LED’s power needs. Also, connecting the dimmer and LED right is key.
Following these steps, TRIAC dimmers can change LED brightness smoothly, without blinking or other bad effects. Plus, they fit with many LED lights and bulbs.

Leading Edge Dimming Made Simple
In the past, leading edge dimmers were used with normal and spotlight bulbs. Made for these bulbs, they use lots of power, which means they don’t always work with low-energy LEDs.
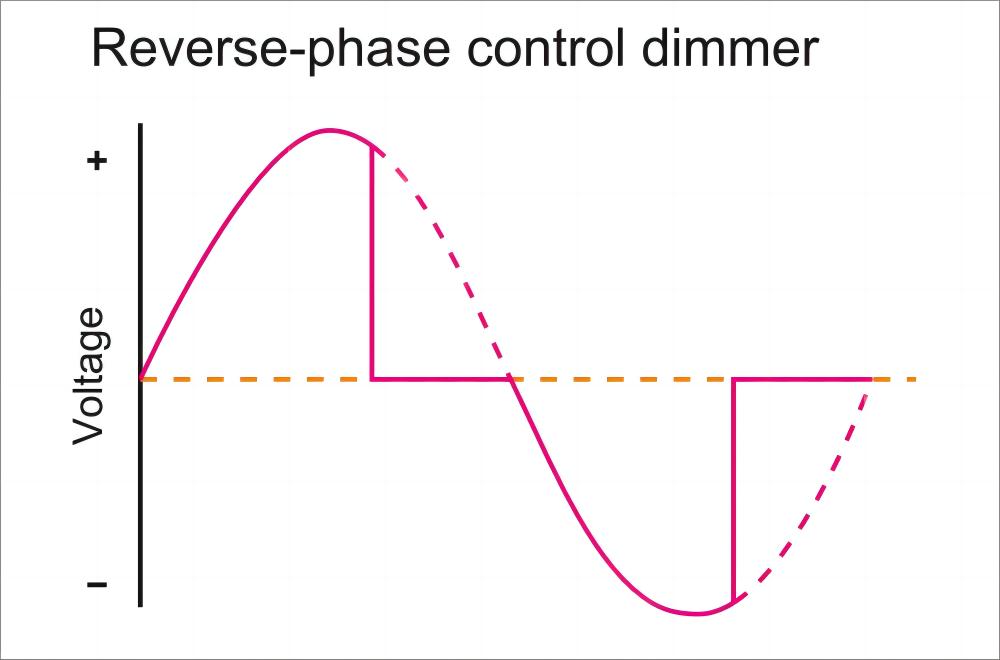
For LEDs, remember that they use little power. So, they might not meet the power needs of the dimmers. Though LEDs use less energy, they give a lot of light, maybe too much for some dimmers. For dimming LEDs, trailing-edge dimmers, which react better to power changes, are best.
Understanding the Trailing Edge Idea
Today’s trailing edge dimmers are better than the older leading-edge ones. They dim more smoothly and have less buzzing.
They need less power, so they’re good for LEDs. When using them with LEDs, follow the 10% rule. For example, a 400W dimmer can handle 40W of LED lights, but 400W of normal bulbs.
Trailing-edge dimmers work well with low-power lights, giving the dimming we want without needing lots of power.
Leading vs. Trailing-edge Dimmers: Main Points
Leading-edge dimmers, used before with normal, spotlight, or wired bulbs, were picked for being easy and cheap. Often named “TRIAC dimmers” because of their switch, they control power use. But, they need a lot of power, so they don’t always fit with low-power LEDs or CFLs today.
Trailing-edge dimmers work silently and smoothly, fitting different building styles. Needing less power, they’re great for circuits with small, energy-saving bulbs.
Understanding TRIAC LED System and Setting It Up
Adding a TRIAC helps change an LED’s brightness. The TRIAC, a part with three ends, needs power on its gate end to turn on. When power is off, it turns off.
Because it can finely control an LED’s power, the TRIAC is great for this. To set up a TRIAC dimmer at home, first change your normal light switch. Join the wall’s black wire to the dimmer’s same colored wire. Then, connect the dimmer’s white wire to the wall’s white one. Last, link the dimmer’s green ground wire to the wall’s plain copper wire.
What is Dimming?
Dimming is changing light brightness with just a switch. There are many types of dimming devices available now.
These devices include Triac dimmers, LED dimmers that work between 0–10 V, and pulse width modulation (PWM) dimmers. Each type changes the current, voltage, and frequency in its way, affecting the light from the source.
In the past, Triac dimming was used for regular and small fluorescent bulbs. But now, it works well with LEDs too. Triac dimming has a specific way it works.
Dimming starts at AC phase 0 and goes on until the Triac device is turned on, causing a big drop in input voltage. The angle of conduction changes the voltage shape, making a new shape different from the starting voltage.
Using a certain direction rule, the needed power for the usual load is less. This then lowers the output voltage value (in basic loads).
People in the industry like the Triac dimmer because it’s accurate, efficient, small, light, and works from afar. So, many companies use it. Triac dimming is loved for its low cost, reliability, and low running costs.
About PWM Dimming
PWM, short for pulse-width modulation, is a new way to control analog systems with digital computer output. It works really well.
This method is used in many areas like measuring, talking, power control, changing, and especially, LED lights. Changing analog systems to digital control can save money and energy.
Modern computer chips often have built-in PWM controls, highlighting the ease of digital control. Getting a PWM value is a straight way to check the strength of an analog signal. With detailed counters, the on-off time of the square wave can be adjusted.
Even if the PWM signal is digital, the full DC power might sometimes be there. This causes a voltage or current source that turns on and off regularly, giving power to the analog load.
When the DC power is on, the load is connected. But when off, it disconnects. With the right frequency range, PWM can show any analog value. To understand better, there’s a diagram showing different PWM signals below.
LED 0/1-10v Dimming Explained
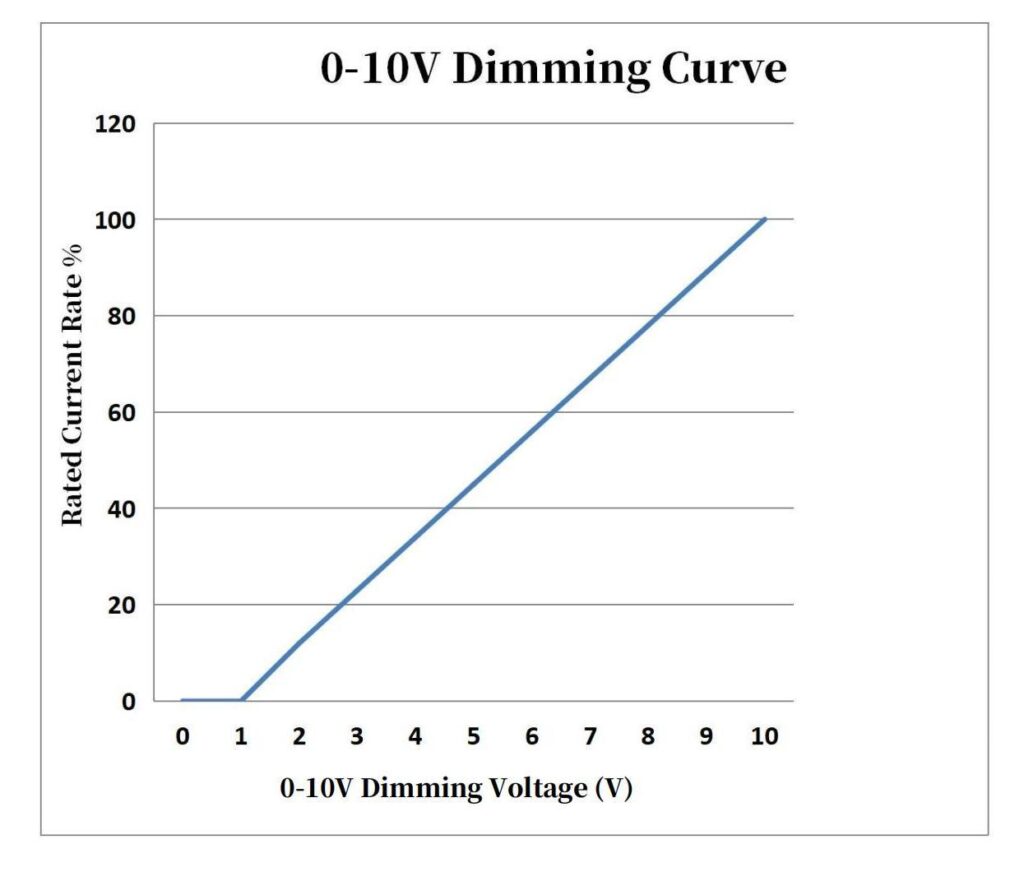
0-10v dimming is an analog way to dim, special because the driver has two ports: +10v and -10v. Usually, a normal Triac dimmer just has one port for both +10v and -10v.
Dimming works by controlling the current sent by the driver. Here, 0V means total darkness and 10V means full brightness. For example, in a resistance dimmer, if voltage is at 1V, current is at 10%. It goes to 100% when voltage is 10V.
It’s key to see the difference between 0–10V and 1–10V. The first one has an on/off switch. The second one doesn’t, so the light is always on, but can be dim.
Learning about DALI Dimming
To set up DALI dimming, a two-wire control cable is needed. After the basic setup, advanced light control systems let you change lighting circuits using set rules. With DALI lighting, things like LED downlights and LED spotlights get full control over their light sources.
What makes DALI special is its great dimming range, better than other new dimming methods. Also, new DALI tech has grown its uses, making it good for managing RGBW and Tunable White lights. If you need to change colors in a detailed way, DALI-standard dimming parts are best.
Getting How a Dimming Curve Works
A dimming curve is a set rule that a dimmer follows when it works. Once the dimmer gets a signal, it makes sure the light matches a set pattern. Think of the fade pattern shown in a picture next to this.
When shopping for dimmers, the dimming curve is important. It shapes the final light and shows how the digital dimmer does its job.
Looking at Different Dimming Patterns
Dimming curves are sorted by how they look on a graph. LEDs, also known as bright little parts, are now popular lights because they use less power, last long, and shine bright.
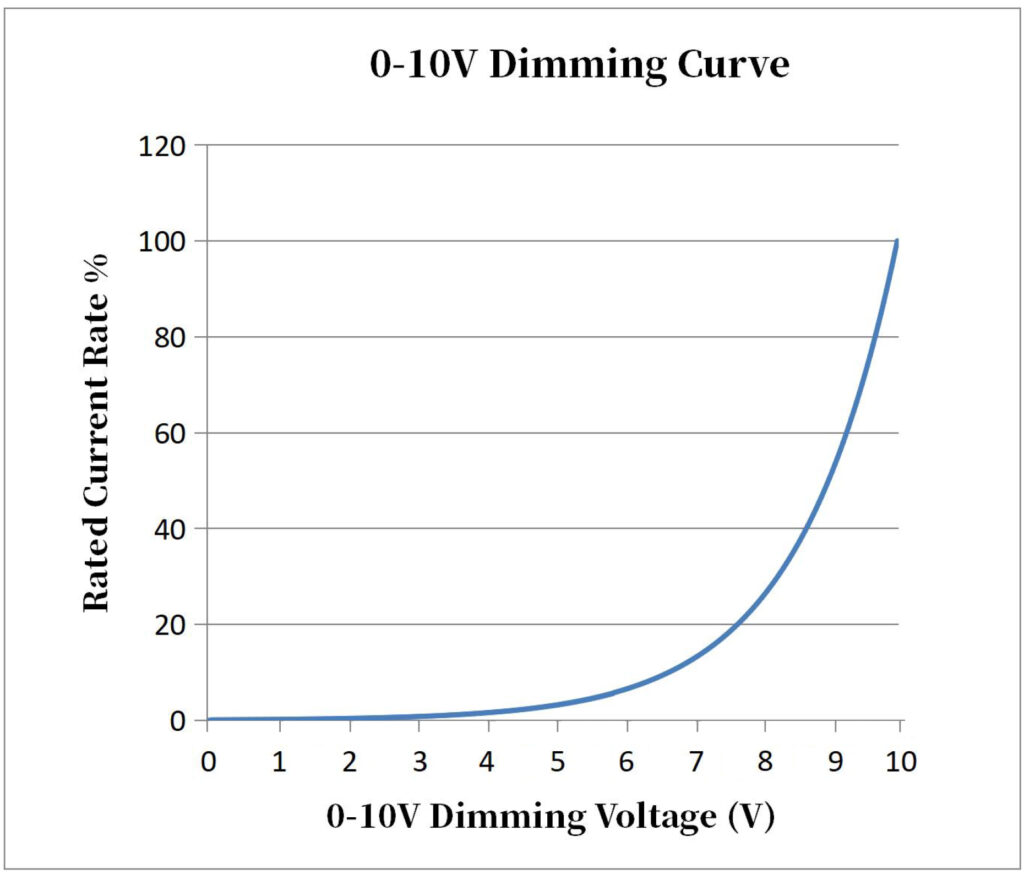
With straight dimming curves, the light matches the power given. Like, a 25% power signal gives 25% light. But, with curve-like dimming, the light changes as power levels go up. When light is dim, the signal to its driver changes slowly. But, when it’s bright, the change is fast.
Dimmers can be set with shapes like the “S” shape or a “soft straight” shape. These power ranges, called “sliders,” help give more control over part of the total power range. For the best look, especially in buildings, picking “straight” or “curve-like” for all devices is best.
Good & Bad of Using TRIAC Dimmers with LEDs
TRIAC dimming has many good sides like being efficient, adjusting well, being light, small, and easy to use with a remote. Right now, it’s a popular dimmer type you can buy.
A big plus, with LED lights, is that it’s cheap to use. But, TRIAC dimmers have issues too. They can’t dim all the way sometimes. Even at the dimmest, a little power still goes through its switch, which is a problem that’s not fixed yet for LED dimming.
Understanding Leading Edge Dimming Better
In the past, these dimmers were mainly used with normal and halogen lights. They were made for those lights and need a lot of power. So, they don’t work that well with power-saving LEDs.
If you use these dimmers with LEDs, know that LEDs use so little power they might not turn on these dimmers. LEDs, though power-saving, can shine very brightly, maybe too much for some new dimmers. For dimming LEDs, trailing-edge dimmers are better as they react well to power changes.
Getting What Trailing Edge Dimming Is
New trailing-edge dimmers are better than the old leading-edge ones. They fade lights quietly and smoothly and have less issues. They need less minimum power, so they’re great for LEDs.
When dimming LEDs with these, follow the 10% rule. For example, a 400W dimmer can handle 400W of normal lights but only 40W of LED lights. These dimmers are best for dimming lights that don’t need much power, without issues of old dimmers that need lots of power.
Telling Leading-edge and Trailing-edge Dimmers Apart
In the past, leading-edge dimmers, sometimes called “TRIAC dimmers” because of their switch, were chosen for normal, halogen, or special magnetic lights. They were easy to set up and cheap, which made them liked. But, they need too much minimum power for new low-power LEDs or CFLs.
On the other hand, trailing-edge dimmers are quiet, smooth, and made in a detailed way. This makes them fit well in many places. Plus, they work great with setups that use newer, power-saving lights.
Related Products

TRIAC Dimmable LED Drivers 5-240W
FAQ
What is a triac dimmer?
A triac dimmer is an electronic device used to control the voltage and, consequently, the light intensity of incandescent or halogen bulbs. It operates using a component called a “triac” (Triode for Alternating Current) to modulate the voltage supplied to the light source, allowing for a range of brightness levels.
How does a triac dimmer differ from other types of dimmers?
Triac dimmers are distinct from other dimming technologies primarily because they use a triac component to cut off portions of the AC waveform, either at the beginning or the end, to reduce the voltage supplied to the lamp. This contrasts with other dimming methods, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) or variable resistors, which adjust light intensity through different mechanisms. Triac dimmers are particularly popular due to their efficiency and compatibility with many traditional light sources.
Are triac dimmers compatible with all types of light bulbs?
Not all light bulbs are compatible with triac dimmers. While they work exceptionally well with incandescent and halogen bulbs, many LED and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) may not be compatible or may require a specific type of triac dimmer. It’s essential to check the bulb’s specifications or manufacturer’s recommendations before pairing it with a triac dimmer to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What are the benefits of using a triac dimmer in lighting systems?
Triac dimmers offer several advantages in lighting systems:
Energie-efficiëntie: By reducing the voltage supplied to the light source, triac dimmers can lead to energy savings, especially when lights are frequently operated at reduced brightness.
Ambiance Control: They allow users to adjust the light intensity to create the desired ambiance or mood in a room.
Langere levensduur lamp: Dimming lights can extend the lifespan of bulbs, as they operate at lower temperatures and reduced stress.
Cost-Effective: Triac dimmers are generally more affordable than some other advanced dimming technologies, making them a popular choice for many households and businesses.
Are there any potential issues or drawbacks associated with triac dimmers?
While triac dimmers offer numerous benefits, there are potential issues to be aware of:
Compatibility Issues: As mentioned earlier, not all light sources, especially some LEDs and CFLs, are compatible with triac dimmers. Using an incompatible bulb can lead to flickering, reduced bulb life, or even damage.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Triac dimmers can produce EMI, which might interfere with other electronic devices in proximity.
Noise: Some triac dimmers can produce a humming or buzzing sound, especially at lower dimming levels. This noise is often more noticeable with certain types of bulbs or lower-quality dimmers.
Heat Production: Triac dimmers can generate heat, especially when dimming high-wattage bulbs. It’s essential to ensure adequate ventilation and avoid installing them in confined spaces.










