Hey there! As someone who’s spent years optimizing facility lighting, I know firsthand how crucial effective lighting control is. How does 0-10V dimming impact your facility’s lighting performance? Let’s dive into the nuts and bolts of this technology and see how it can make a world of difference in your facility.
0-10V Dimming Overview
0-10V dimming is a method of controlling the brightness of LED lights by varying the voltage between 0 and 10 volts. This straightforward system allows for smooth dimming operations, helping facilities achieve energy savings and customized lighting levels. Despite its benefits, compatibility issues with different dimmers and drivers can pose challenges. But like anything, it’s not without its quirks—compatibility issues with different dimmers and drivers can be a bit of a headache.
Understanding 0-10V Dimming
0-10V dimming operates by using a low-voltage direct current (DC) signal to control the intensity of lighting fixtures. This system functions on a straightforward principle: as the voltage decreases, the light output dims. When the voltage is at 10 volts, the light operates at full brightness. As you dial down the voltage to 0 volts, the light gradually dims until it reaches its minimum brightness or turns off completely.
This method of dimming is one of the earliest and simplest forms of lighting control, making it a popular choice in many commercial and industrial facilities. Its simplicity lies in the analog nature of the control—there’s no complex digital processing involved, just a straightforward adjustment of voltage that results in a corresponding change in light intensity.
One of the key reasons 0-10V dimming remains widely used is its reliability and ease of integration with various types of lighting fixtures, especially LED lights. It’s a versatile system that can be implemented in different settings, from office buildings and warehouses to retail spaces and manufacturing plants.

What are the benefits of 0-10V dimming?
0-10V dimming has a bunch of benefits that can make your life a lot easier:
- Smooth dimming operation: This system allows for smooth operation at different light levels, including 10%, 1%, and even 0.1%. It’s all about flexibility—whether you need bright light for detailed work or a softer glow for ambiance, 0-10V dimming has got you covered.
- Energy savings: By dialing down the light intensity when full brightness isn’t needed, we can save a ton of energy. This means lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint, which is a win-win.
- Enhanced ambiance: Being able to adjust the light levels based on specific needs can significantly improve the overall environment. Whether it’s boosting productivity in a workspace or creating a cozy atmosphere in a lounge area, the right lighting makes all the difference.
- Extended lifespan of lighting fixtures: Running lights at lower levels reduces stress on the LEDs, extending their lifespan and cutting down on maintenance costs.
What is the problem with 0-10V dimming?
Now, I won’t sugarcoat it—0-10V dimming isn’t perfect. Here are a few hiccups you might run into:
- Lack of standardization: The biggest issue is the lack of a fully standardized approach, which can lead to uneven dimming across different LED luminaires. It’s a bit like trying to use different brands of remote controls with one TV—not always a smooth experience.
- Compatibility issues: Poor compatibility among dimmers and drivers can mean frequent changeouts, causing delays and extra costs. It’s frustrating, but with the right planning and products, we can usually navigate around these obstacles.
- Wiring requirements: Proper wiring and installation are crucial for the system to function correctly. This can add to the initial setup complexities, but once it’s in place, you’re golden.
What is the major disadvantage of controlling different groups of luminaires using a 0-10V dimming system?
The main drawback here is the compatibility issue between different standards (IES Standard 60929 Annex E and Standard ESTA E1.3). This incompatibility means that dimmers might not work properly with all drivers, leading to inconsistent dimming performance and potential maintenance challenges. It’s a bit of a pain, but understanding these standards can help us choose the right components from the get-go.

Does dimming LED lights reduce power consumption?
- Energy reduction: Absolutely. The brighter an LED, the more energy it consumes. So, dimmed LEDs use less energy, which not only lowers operational costs but also supports our sustainability goals. It’s like turning down the volume on your speakers—you’re still getting the sound, just not at full blast.
Comparison with Other Dimming Methods
Let’s compare 0-10V dimming with some other common methods:
- Triac Dimming vs. 0-10V Dimming: Triac dimming is often used for incandescent and halogen lights and works by cutting parts of the AC wave to reduce light output. In contrast, 0-10V dimming is more suitable for LED systems, offering smoother and more precise control.
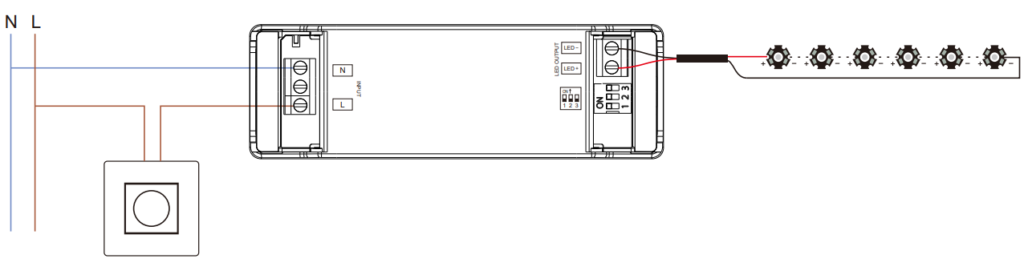
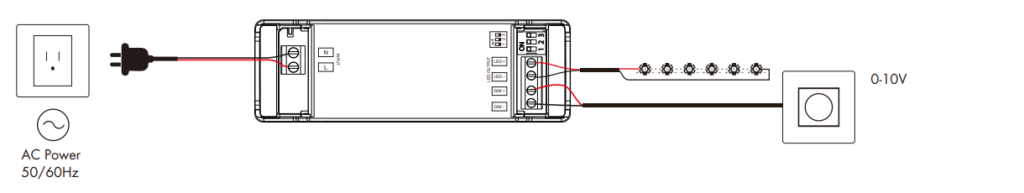
- 1-10V Dimming vs. 0-10V Dimming: While similar, 1-10V dimming is typically used in Europe and has slightly different voltage ranges and control methods. Both methods offer similar benefits, but it’s essential to choose the one compatible with your system’s requirements.
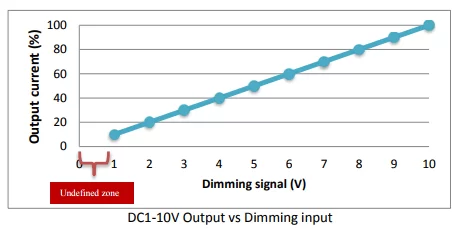
Here is a table comparing 0-10V, 1-10V, and TRIAC dimming methods:
| ลักษณะเฉพาะ | 0-10V Dimming | 1-10V Dimming | TRIAC Dimming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Signal Type | Analog, low-voltage DC (0-10V) | Analog, low-voltage DC (1-10V) | Digital, AC phase control |
| Typical Use Case | LED lighting in commercial and industrial | LED lighting, commonly in Europe | Incandescent, halogen, and some LED lights |
| Voltage Range | 0 to 10 volts | 1 to 10 volts | Adjusts phase angle of AC supply |
| ช่วงลดแสง | Smooth dimming from 100% to 0% | Smooth dimming from 100% to approximately 10% | Smooth dimming from 100% to near 0% |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate, requires compatible wiring | Moderate, requires compatible wiring | Low, uses existing wiring |
| Compatibility | Compatible with most commercial LED drivers | Often used in specific regions (Europe) | Compatible with most traditional bulbs and some LEDs |
| Energy Efficiency | High, suitable for energy-saving applications | High, suitable for energy-saving applications | Moderate, less efficient with LEDs compared to analog dimming |
| Standardization Issues | Some compatibility issues between different brands | Fewer standardization issues in regions where used | Standardized, widely understood |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Smoothness of Dimming | Very smooth, good for varying light levels | Smooth, but may not dim below 10% | Smooth, but can have flickering issues with some LEDs |
| Common Applications | Offices, warehouses, retail spaces | Similar to 0-10V, but more regional | Residential, smaller commercial spaces |
| Maintenance Needs | Low, but requires careful component selection | Low, but requires careful component selection | Low, straightforward maintenance |
Energy Savings and Maintenance Implications
- Energy Savings: Dimming can lead to significant energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. By using less energy, we can achieve more sustainable operations.
- Maintenance: Running lights at reduced levels can extend the lifespan of LED fixtures, lowering maintenance needs and costs. Less frequent replacements and repairs mean less downtime and fewer disruptions to your operations.
Relevant Standards and Regulations
Adhering to relevant standards such as IES Standard 60929 Annex E and ESTA E1.3 ensures optimal performance and compliance. Understanding these standards helps us select compatible components and achieve the best results from your dimming system.
Summary
In conclusion, 0-10V dimming can greatly enhance your facility’s lighting performance through energy savings, customizable light levels, and extended fixture lifespan. However, it’s crucial to address compatibility issues and adhere to standards for optimal results. Considering these factors can help you implement a more efficient and effective lighting control system.
So, if you’re thinking about upgrading your facility’s lighting, 0-10V dimming is definitely worth considering. It’s got its quirks, but with the right setup and a bit of know-how, it can make a huge difference. If you have any questions or need help figuring out the best solution for your facility, don’t hesitate to reach out—I’m here to help!
We are boqi, which has 0-10V dimmable LED Drivers and compatible 0-10V dimmers.









