Introduzione
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) have revolutionized the lighting industry with their energy efficiency and longevity. However, to function optimally, LEDs require a specific type of power supply known as an LED driver. This article delves into the world of LED drivers, their types, and their applications, particularly in dimming LED strip lights.


Understanding LED Drivers
Driver LED are specialized power supplies that provide the necessary current and voltage for LED operation. They come in two main types: constant current and constant voltage drivers.
Types of LED Drivers
Constant Current LED Drivers
Constant current LED drivers deliver a fixed output current and a variable output voltage range. This means that even when the LED voltage changes, the current remains constant.
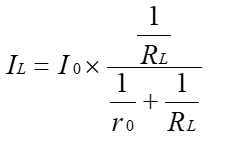
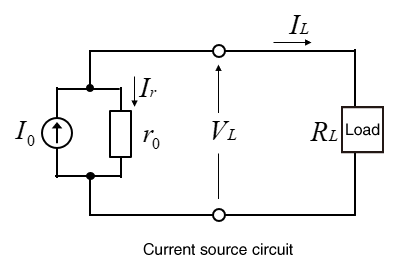

Driver LED a tensione costante
On the other hand, constant voltage LED drivers are designed for a single DC output voltage. They maintain a constant voltage regardless of the current flowing through them. These drivers are suitable for LED strips, which usually have a current limiting resistor in series with the LED.

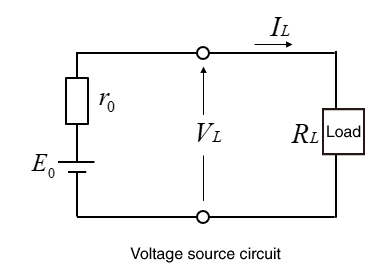
Dimming LED Strip Lights
LED strip lights offer flexibility in lighting design and can be dimmed to create the desired ambiance. However, dimming these lights requires the right power source and configuration.

Techniques for Dimming
There are several techniques for dimming constant voltage LED strip lights, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In general, either a non-dimmable (with an extra controller) or a dimmable driver can be used to dim an LED strip light.
Non-Dimmable Light Source
This approach is straightforward as it does not require any additional wiring. Dimming is achieved on the DC side of the driver using a controller connected inline between the driver and the LED strip light.
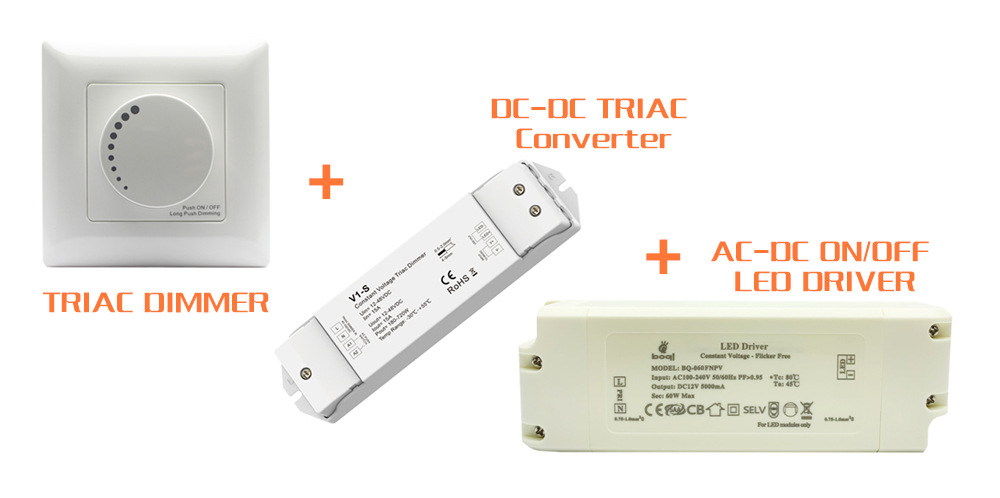
Dimmable LED Driver
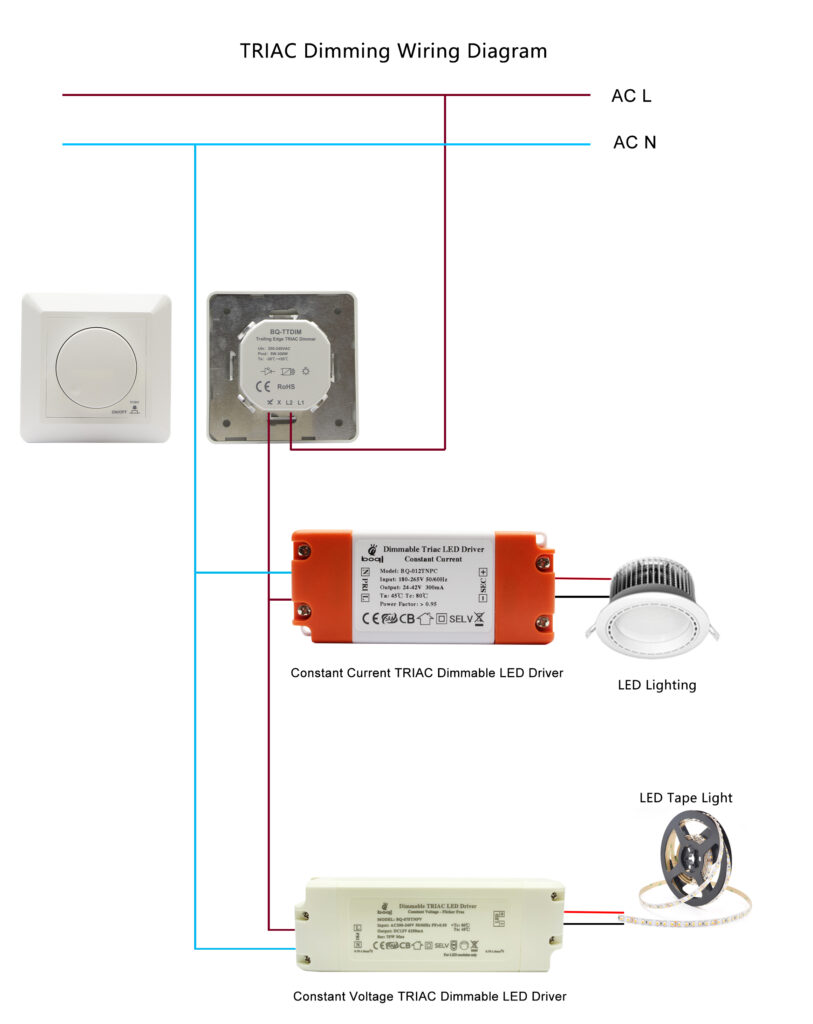
There are two kinds of constant voltage dimmable drivers: phase-cut dimmable LED drivers and those utilizing a signal control in the driver’s control wires.


Pros and Cons of Different Dimming Methods
Each dimming method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Non-Dimmable Driver
Non-dimmable drivers are often less expensive and easier to obtain. However, they require a controller to operate, which can be a disadvantage.
Driver LED dimmerabili a taglio di fase
That is vital to choose a good TRIAC and phase-cut dimmable led driver.
Pros of Phase-Cut Dimmable LED Drivers
Phase-cut dimmable drivers are perfect for upgrading older systems as they require no additional wiring, and are compatible with standard wallplate dimmers, making them a convenient option for retrofit applications.
Cons of Phase-Cut Dimmable LED Drivers
These drivers can be more expensive than other types of dimmable drivers and may interfere with other electrical drivers. They also require a compatible dimmer, which can limit their use in certain applications.
Signal Input Dimmable Driver
Signal input dimmable drivers are cost-effective and offer versatile design options. However, they may not be compatible with existing systems and require an additional pair of signal wires to be installed.

Pros of Signal Input Dimmable Drivers
These drivers offer a high degree of control over the light output. They can also be integrated with home automation systems for advanced lighting control.
Cons of Signal Input Dimmable Drivers
Signal input dimmable drivers require additional wiring for the signal input, which can add to the complexity of the installation. They may also not be compatible with existing lighting systems.
Signal Input Dimmable Drivers can be PWM LED Driver or 0-10V LED Driver.
Importance of PWM Output
PWM, or Pulse Width Modulation, is a technique used in dimming and controlling LED lights. It allows for a wide range of brightness by altering the amount of time the signal is ON or OFF.
Che cos'è la dimmerazione PWM?
In PWM dimming, an LED will receive either full voltage or no electricity at all, allowing for precise control over brightness levels.
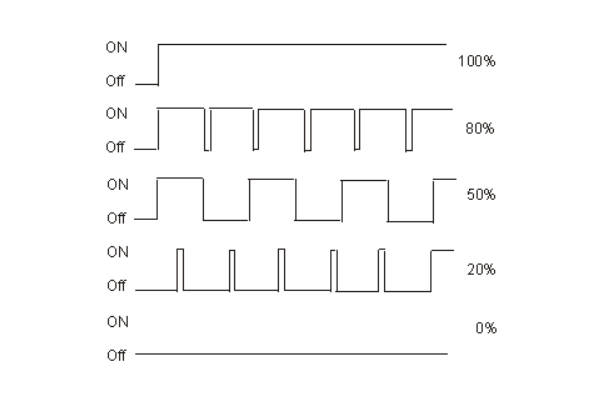
Significance of PWM Output
PWM output solves the challenge of load matching, ensuring constant and full-range dimming regardless of the driver capacity and/or load. It also allows for equal dimming levels when using different size drivers controlled by the same driver.
Importance of 0-10V Output
Il Dimmerazione 0-10V control method is widely used in commercial and industrial lighting applications due to its simplicity and reliability. It allows for precise control over the light output, enabling energy savings and improving the flexibility of lighting design.
Understanding 0-10V Output
0-10V is a type of analog lighting control signal used in dimming applications. The concept is simple: a control signal of 0V corresponds to the minimum light output, and a control signal of 10V corresponds to the maximum light output. The light output is linearly proportional to the control signal voltage.
Advantages of 0-10V Dimming
0-10V dimming offers several advantages. It provides smooth, flicker-free dimming, enhancing the visual comfort. It also allows for easy integration with building management systems for advanced lighting control. Moreover, 0-10V dimming can contribute to energy savings by adjusting the light output based on the needs of the space.
Disadvantages of 0-10V Dimming
Despite its advantages, 0-10V dimming also has some limitations. It requires additional control wiring, which can increase the complexity of the installation. Also, not all LED fixtures are compatible with 0-10V dimming, which can limit its applicability.

Comparison between Constant Voltage and Constant Current Driver
LED drivers come in two main types: constant current and constant voltage drivers. A constant current LED driver delivers a fixed output current and a variable output voltage. This means that even when the LED voltage changes, the current remains constant. On the other hand, a constant voltage LED driver maintains a constant voltage regardless of the current flowing through it. This type of driver is typically used for LED strips, which usually have a current limiting resistor in series with the LED.

Conclusione
Understanding LED drivers and their applications in dimming LED strip lights is crucial for optimal LED performance. Whether you choose a constant current or constant voltage driver, or a non-dimmable or dimmable driver, depends on your specific needs and constraints. Regardless of the choice, the importance of PWM output cannot be overstated for its role in achieving precise and consistent dimming.

Domande frequenti
What is an LED driver?
An LED driver is a device that provides the necessary power (in terms of current and voltage) for an LED to function optimally.
What is the difference between a constant current and a constant voltage LED driver?
A constant current LED driver delivers a fixed output current and a variable output voltage, ensuring the current remains constant even when the LED voltage changes. On the other hand, a constant voltage LED driver maintains a constant voltage regardless of the current flowing through it.
How can I dim my LED strip lights?
You can dim your LED strip lights by using the right power source and configuration, which could involve a non-dimmable (with an extra controller) or a dimmable driver.
What are the pros and cons of different dimming methods?
The pros and cons of different dimming methods vary. Non-dimmable drivers are often less expensive but require a controller to operate. Phase-cut dimmable drivers are perfect for upgrading older systems but can be expensive. Signal input dimmable drivers are cost-effective and offer versatile design options but may not be compatible with existing systems.
What is PWM output and why is it important?
PWM, or Pulse Width Modulation, output is a technique used in dimming and controlling LED lights. It’s important because it allows for a wide range of brightness by altering the amount of time the signal is ON or OFF, ensuring constant and full-range dimming regardless of the driver capacity and/or load.







